The lives of Roman priests and priestesses are shrouded in mystery, revealing a world where religious devotion meets societal expectations. By exploring the hidden lives of these revered figures, we can uncover the secrets, privileges, and responsibilities that shaped ancient Rome.
Understanding the enigmatic role of Roman priests and priestesses helps us grasp the intricate relationship between spirituality and daily life in a civilization deeply rooted in tradition and reverence.
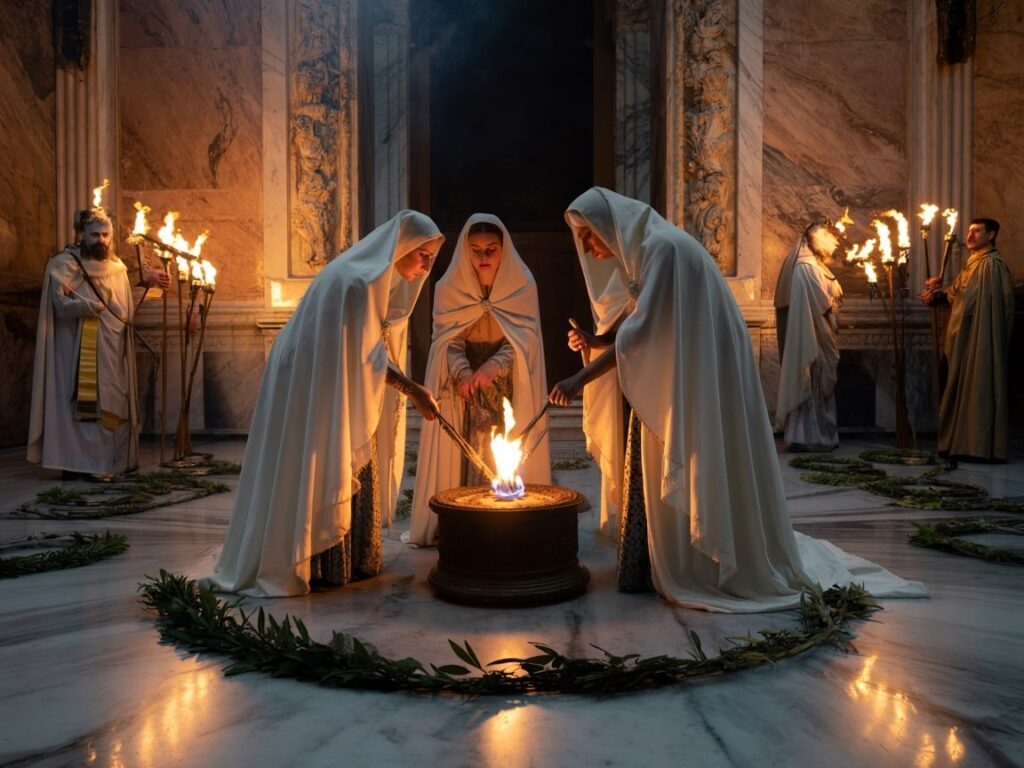

The Vestal Virgins: Keepers of the Sacred Fire
The Vestal Virgins were priestesses in ancient Rome who dedicated their lives to serving Vesta, the goddess of the hearth and home. They held a special and highly respected position in society.
Selection and Service
The process of becoming a Vestal Virgin was strict. Girls between the ages of six and ten were chosen from patrician families, which were the aristocratic class in Rome. Once selected, these young girls were expected to serve as priestesses for a period of 30 years. During this time, they had to follow a strict vow of celibacy — an essential requirement directly linked to their sacred responsibilities.
Duties and Rituals
The main duty of the Vestal Virgins was to ensure that the eternal flame inside the Temple of Vesta never went out. This fire represented the safety and continuity of Rome itself; if it ever extinguished, it was seen as a bad omen threatening the city’s future. Every day, the Vestal Virgins performed rituals with great care, such as:
- Tending to the fire
- Offering prayers
- Making offerings
- Protecting various sacred objects associated with Rome’s spiritual well-being
Consequences of Breaking the Vow
Breaking the celibacy vow had serious repercussions. The chastity of the Vestal Virgins was not just a personal matter but also a political and religious safeguard for Rome. Any violation was viewed as an act of treason against the city and could result in being buried alive in an underground chamber—a punishment intended to prevent spilling their blood, which was forbidden. This severe penalty demonstrated how important their role was and how closely religion was tied to state security.
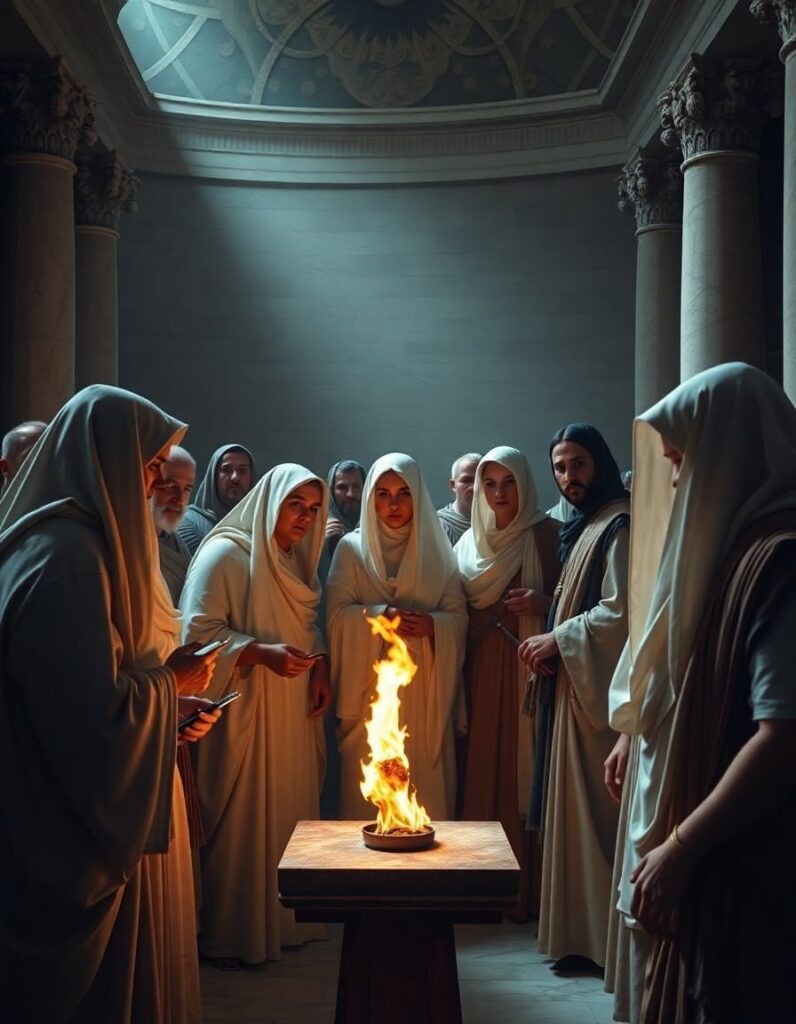
Privileges and Punishments: The Duality of Power for Vestal Virgins
The life of a Vestal Virgin was marked by a striking contrast between exceptional privileges and severe punishments. These women held a unique position in Roman society, unlike any other female role.
Privileges of Vestal Virgins
Vestal Virgin privileges included:
- Legal autonomy: They could own property independently, an unusual right for Roman women.
- Political influence: Vestals had the rare ability to participate in certain civic functions and were granted seats of honor at public games and events.
- Judicial power: They could pardon condemned prisoners or slaves simply by their presence, an extraordinary legal authority.
- Social respect: Their person was considered sacred; harming a Vestal was met with harsh consequences.
Such privileges reinforced their importance not only religiously but socially and politically as well.
Punishments for Vestal Virgins
The flip side involved punishment for treason, particularly if they broke their vow of celibacy—a crime seen as betraying Rome itself. The penalty was:
- Burial alive: A grim form of execution that avoided spilling their sacred blood.
- Public disgrace: This punishment served as a warning to others about the seriousness of their role.
The intense duality of power and vulnerability shaped the Vestal Virgins’ existence, underscoring the high stakes involved in their commitment to Rome’s spiritual welfare.
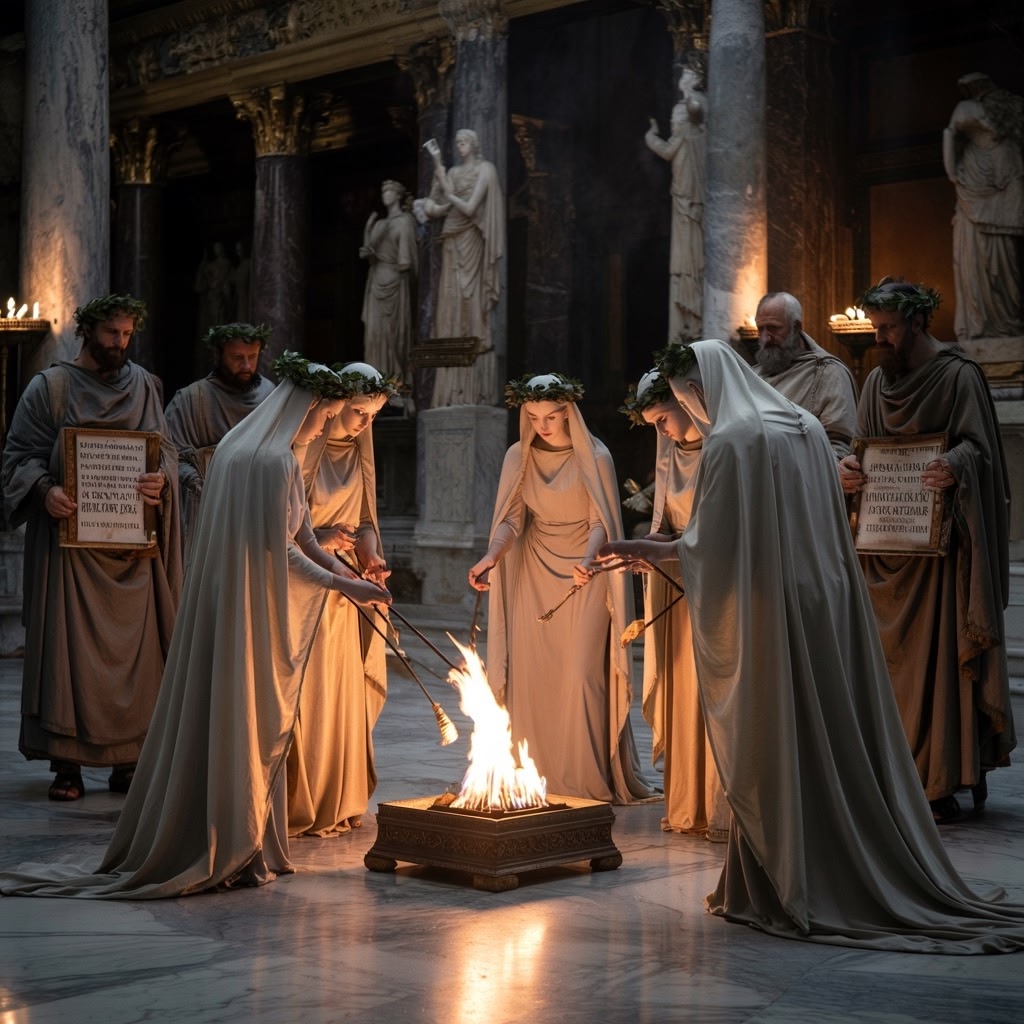

Women in Ancient Rome: A Closer Look at the Legal Powers and Societal Status of Vestal Virgins
The status of women in ancient Rome was generally limited by strict social and legal constraints. Most Roman women were under the authority of a male guardian—father, husband, or closest male relative—and lacked independent legal rights. Their roles were primarily domestic, focused on family and household management, without significant public or political influence.
Vestal Virgins stood apart from this norm, occupying a unique position that granted them exceptional legal powers and societal respect:
- Legal Autonomy: Unlike typical Roman women, Vestal Virgins could own property outright, manage their own finances, and draft wills without male approval.
- Judicial Influence: They held the rare power to pardon condemned prisoners simply by their intervention, symbolizing their profound impact on justice and mercy.
- Political Privileges: Vestals had the right to vote—a privilege denied to most women—and were accorded special seats at public games and events.
- Religious Authority: Their sacred role as keepers of Vesta’s fire made them vital to Rome’s spiritual well-being, granting them a revered status that transcended ordinary gender roles.
This distinct combination of powers highlights their dual identity as both religious servants and influential legal figures within Roman society. The legal powers of Vestal Virgins underscore how religion offered an extraordinary avenue for women’s agency in an otherwise patriarchal world.
The Secret Lives of Roman Priests and Priestesses often reveal these intersections between faith, law, and gender—showing how some women navigated complex social dynamics through sacred office.
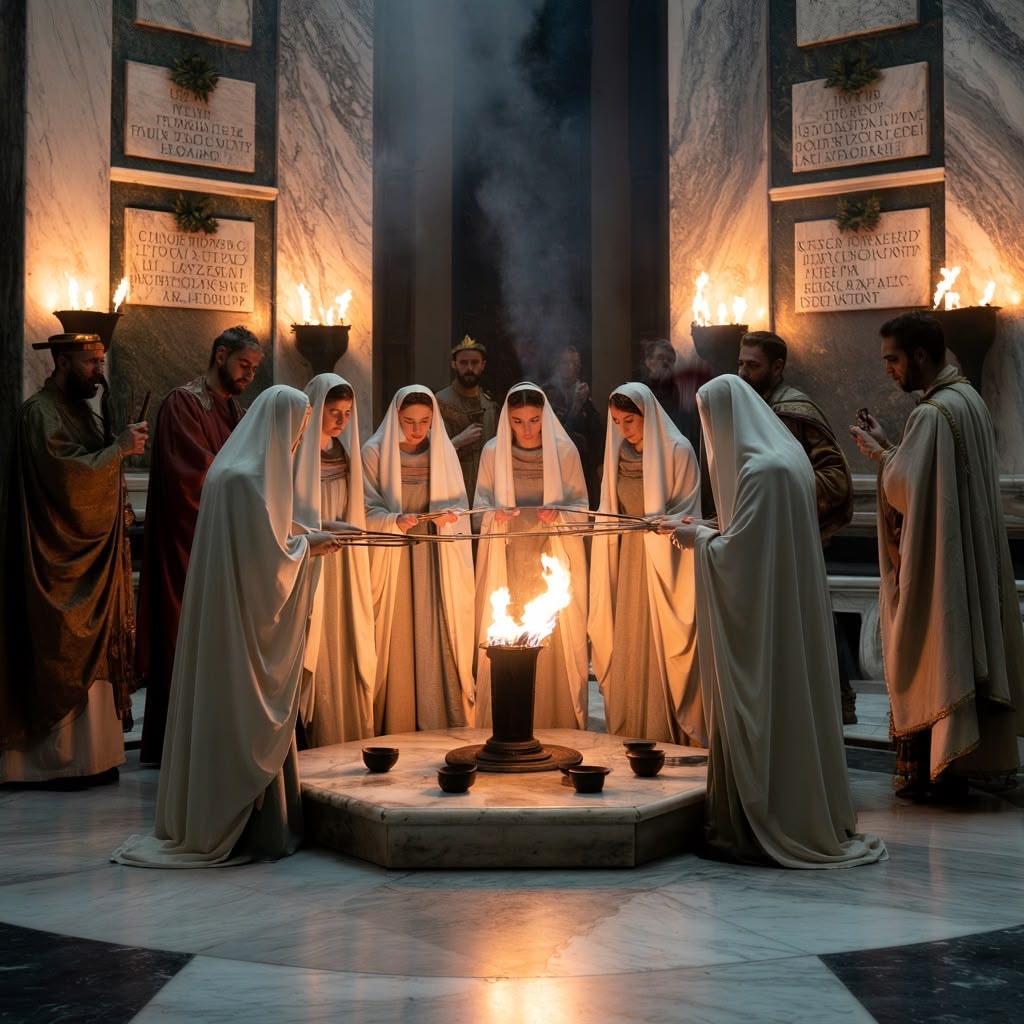

Balancing Act: The Lives of Other Roman Priests and Priestesses Beyond the Altar
Roman priests and priestesses, apart from the famed Vestal Virgins, held a wide range of religious duties that connected them deeply to the spiritual life of the city. Their responsibilities included performing sacrifices, overseeing festivals, interpreting omens, and maintaining sacred rites crucial for Rome’s divine favor. These roles demanded strict adherence to ritual purity and precise observance of tradition.
Unlike the Vestals, most priests and priestesses did not live cloistered lives within temple precincts. They often maintained private lives alongside their public religious functions. This dual existence required a delicate balancing act between religious duties and personal affairs—marriage, family obligations, property management—while conforming firmly to social norms. For example:
- Pontifices, senior priests, often came from elite families and juggled political careers with their sacred tasks.
- Flamines, priests assigned to particular deities like Jupiter or Mars, adhered to strict lifestyle rules but still participated in public life.
- Female priestesses other than Vestals had less rigid restrictions but were expected to embody moral conduct aligned with Roman values.
The complexity of these roles meant that their authority was respected but also scrutinized. Their ability to navigate both sacred rituals and everyday societal expectations shaped how religion integrated into the broader fabric of Roman life. This balance preserved the sanctity of their office while allowing participation in Rome’s civic world.
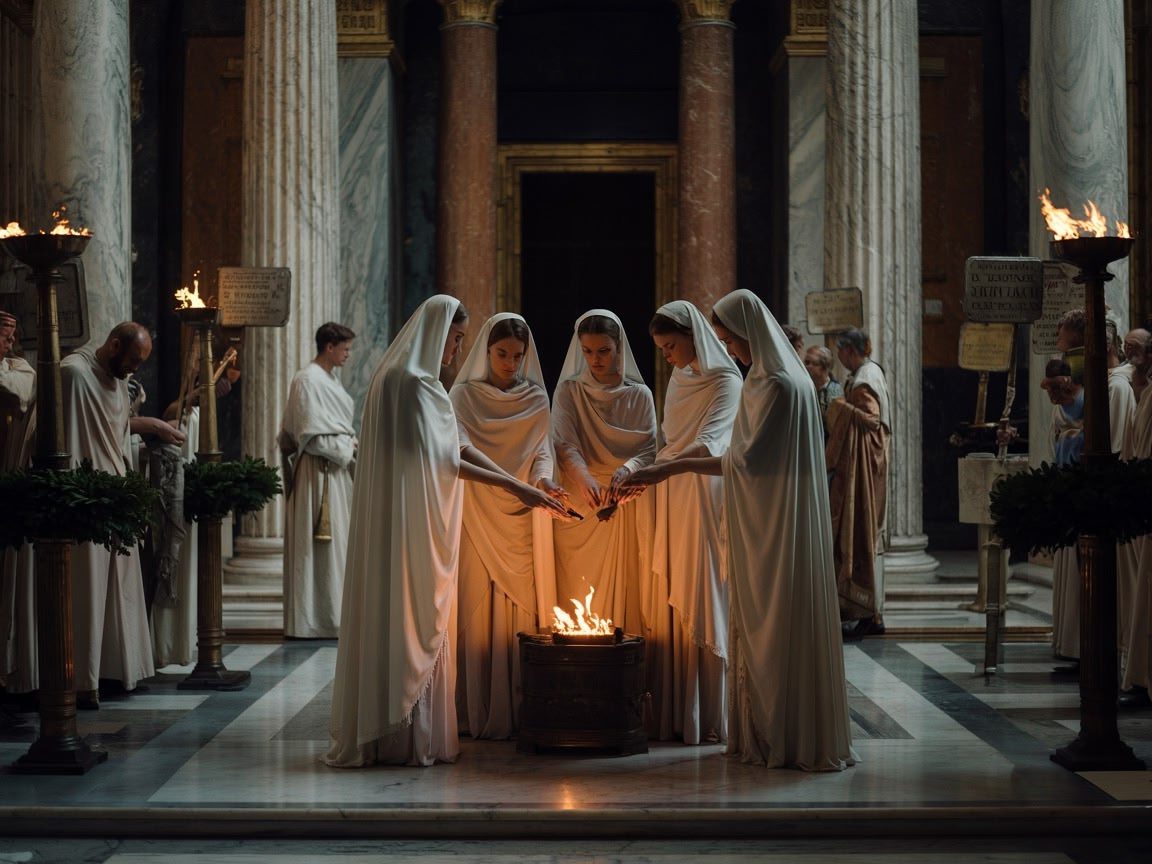

The Veil of Secrecy: Unraveling the Mysteries Surrounding Roman Priests’ and Priestesses’ Private Lives
The daily lives of Roman priests and priestesses were shrouded in secrecy, with rituals and practices kept hidden from the public eye. Their roles involved intricate ceremonies and connections to divine entities that were not openly shared with the masses.
These individuals held sacred knowledge passed down through generations, often participating in esoteric rites that were inaccessible to common citizens. The aura of mystery surrounding their activities added to their enigmatic allure within Roman society.
Legends surrounding their private lives
Over time, numerous legends and myths have emerged regarding the private lives of Roman priests and priestesses. Stories of divine encounters, prophecies, and supernatural powers attributed to these religious figures have persisted throughout history.
Some accounts depict romantic entanglements or forbidden relationships that transcended societal norms, highlighting the complex interplay between personal desires and religious obligations in their lives.
By delving into these enigmatic aspects of Roman priests’ and priestesses’ private lives, we gain a deeper understanding of the mystical world they inhabited and the enduring legacy they left behind.
Public Functions and Cultural Significance: The Role of Roman Priests and Priestesses in Shaping Society
The Secret Lives of Roman Priests and Priestesses played a crucial role in shaping ancient Roman society through their involvement in religious traditions and maintenance of societal order:
Importance of Roman Priests and Priestesses in Maintaining Religious Traditions
- Roman priests and priestesses were instrumental in conducting elaborate rituals and ceremonies dedicated to various gods and goddesses.
- They were responsible for ensuring the continuity of religious practices that were deeply ingrained in the fabric of Roman culture.
- Their ceremonial duties helped foster a sense of spiritual connection among the people and reinforced the significance of divine favor in everyday life.
Their Role in Upholding Societal Order in Ancient Rome
- Beyond their religious functions, Roman priests and priestesses also played a role in upholding societal norms and values, such as those outlined in the Mos maiorum, which emphasized traditional customs.
- Their guidance was sought on matters of morality, ethics, and social conduct, contributing to the maintenance of order within the community.
- By embodying virtues and setting examples through their actions, they served as moral compasses for the Roman populace, influencing behavior and fostering unity.
The intricate interplay between religious practices and societal structures underscored the profound impact that Roman priests and priestesses had on shaping the cultural landscape of ancient Rome.
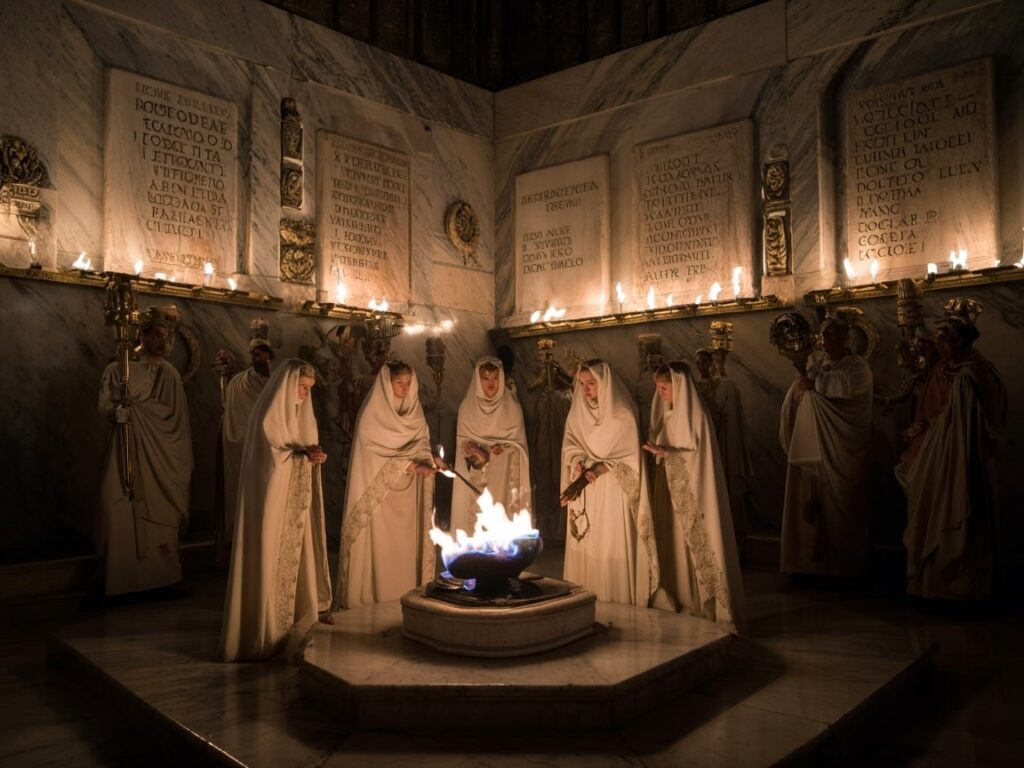

Conclusion
The legacy of Roman priests and priestesses echoes through history, shaping the religious and societal fabric of ancient Rome. Their mysterious lives, filled with secrecy yet marked by deep influence, continue to fascinate modern minds. By exploring their hidden world, we discover not only tales of worship and ceremony but also insights into the complex history of a past age. As we reflect on their impact, let’s embrace the excitement of uncovering more secrets about the lives of Roman priests and priestesses, for they possess the knowledge to reveal historical marvels.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Who were the Vestal Virgins and what was their significance in ancient Rome?
The Vestal Virgins were priestesses dedicated to the goddess Vesta, responsible for maintaining the sacred fire of Vesta. They took a vow of celibacy and played a crucial role in Rome’s religious traditions, symbolizing purity and safeguarding the city’s spiritual well-being.
What privileges and punishments did Vestal Virgins experience during their service?
Vestal Virgins enjoyed unique privileges such as legal powers and societal respect uncommon for women in ancient Rome. However, breaking their vow of celibacy or committing treason led to severe punishments, including harsh penalties reflecting the duality of their power and responsibility.
How did the legal powers and societal status of Vestal Virgins compare to other women in ancient Rome?
Unlike most women in ancient Rome who had limited rights, Vestal Virgins held significant legal powers and a revered societal status. Their roles granted them autonomy and influence, distinguishing them within the patriarchal structure of Roman society.
What were the roles and challenges faced by other Roman priests and priestesses beyond the Vestal Virgins?
Other Roman priests and priestesses balanced religious duties with their private lives while adhering to social norms. They performed various rituals essential to maintaining Rome’s religious traditions but often kept aspects of their personal lives secret due to societal expectations.
Why are the private lives of Roman priests and priestesses described as mysterious or secretive?
The private lives of Roman priests and priestesses remain shrouded in secrecy due to their exclusive roles, societal restrictions, and legends that surround them. This veil of secrecy highlights the enigmatic nature of their existence beyond public religious functions.
What impact did Roman priests and priestesses have on society and culture in ancient Rome?
Roman priests and priestesses played a vital role in upholding religious traditions, which were integral to maintaining societal order. Their public functions reinforced cultural values, contributed to social cohesion, and left a lasting legacy influencing history and culture beyond their time.

